Inside the Elaborate Scheme to Transport a Chinese Power Plant to Russia’s Arctic Undetected
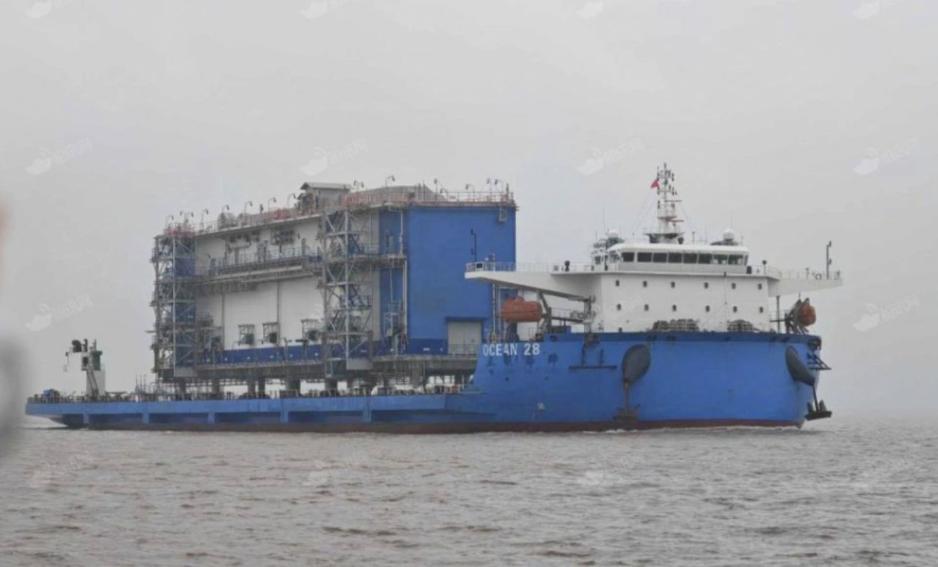

Heavy lift vessel Ocean 28 departing from Zhangjiagang with a substation module on September 23, 2024. (Source: HNN)
In a desperate attempt to salvage Russia’s largest liquefied natural gas project a small fleet of Chinese cargo vessels has set sail for the Arctic. Aboard is a massive power plant for Novatek’s Arctic LNG 2 project, assembled at China’s Wison New Energies for the past two years. With only weeks left before winter sea ice will make the route impassible the delivery is a race against time and against Western sanctions.
It is the summer of 2022, months after the full scale invasion of Ukraine, and Russia's largest producer of liquefied natural gas finds itself in a tight spot.
The future of Novatek’s flagship gas project looks increasingly uncertain following the departure of Western technology partners.
American company Baker Hughes has only delivered four highly sophisticated gas turbines, Novatek needs almost two dozen. Think massive airplane engines found on a Boeing 777.
Novatek succeeds in redesigning the first production line to run on only four Western turbines, but the picture is much bleaker for the second production line under construction at that time.
Without the turbines the project is effectively dead in the Arctic water.
The company turns to its Chinese engineering and construction partner Wison New Energies. The solution is a massive onshore power plant running on older, less efficient Chinese turbines.
Wison's main construction yard begins construction on the power generation modules in December 2022.
Fast forward to the summer of 2024. Four power generation modules and one substation, each the size of a midsize apartment complex, have been completed and are awaiting pick up at Wison’s Zhoushan yard.
Now the key question is: How to deliver the large structures to the Arctic without detection.
The U.S. has been adamant about stopping Russian LNG expansion, including Novatek’s Arctic LNG 2 project.
Thus far Wison has escaped U.S. sanctions. Earlier during the summer of 2024, when the U.S. sanctioned a neighboring shipyard, Wison quickly recalled a vessel en route to Russia carrying equipment for the Arctic project, possibly for fear of repercussions.
In June 2024 Wison announced it would cease all cooperation with Russia.
But construction on the power generation modules and substation for the onshore power plant seemingly continued.
The first module, the substation, was picked up by a heavy lift vessel in late August 2024, a specialized vessel designed to carry large structures. Two additional modules, both related to power generation, were loaded less than two weeks later.
What follows is a detailed account of an elaborate scheme to transport elements of the onshore power plant to the Russian Arctic undetected.
The operation includes using a half dozen vessels, unloading and reloading the modules in various Chinese ports to obscure their origin, and renaming as well as repainting vessels mid-voyage to confuse anyone who may be watching.
Novatek and Wison: A Critical Partnership
Wison New Energies has been a key partner for Novatek’s Arctic LNG 2 project, manufacturing a dozen modules, more than any other Chinese construction yard contracted for the project.
Between 2021 and 2023 it delivered eight modules forming the core of each production line. An attempt to transfer the final modules was canceled in July 2024, likely for fear of sanctions.
Wison also announced that it would cease all cooperation with Russia and divest from or sell its Zhoushan construction yard.
However, those steps have apparently not been taken.
“The yard has not been sold yet, and they have not completed the divestment. The Arctic LNG 2 modules […] have not been transferred yet,” a person familiar with developments at the Zhoushan yard told HNN on condition of anonymity due to the sensitive nature of the subject.
Wison’s website confirms that the Zhousan yard remains part of the company’s assets.
Following Baker Hughes’ exit Novatek turned to Wison to construct an onshore power plant to deliver the massive energy needs to drive the re-designed liquefaction line, now using an electrical drive.
“Due to the departure of Baker Hughes, Wison provided Novatek with a land-based generator solution using Chinese gas turbines,” the source confirms.
Wison constructed five new modules: Four power generation modules, referred to as PGM1 to PGM4, and one substation. Each module weighing between 5,000 and 7,000 tonnes.
Wison’s Zhoushan yard began working on the onshore power plant (OPP) modules in late 2022. The gas turbines housed inside the modules are provided by Harbin Guanghan Gas Turbine (HGGT), a manufacturer of gas turbines for power generation.
Without the onshore power plant, the second production line of Arctic LNG 2 can not be commissioned.
Five Modules Take Shape at Wison Zhoushan
Throughout 2023 and into 2024 satellite images document the progress Wison makes on the five modules. By summer of 2024 the modules appear to be near completion.
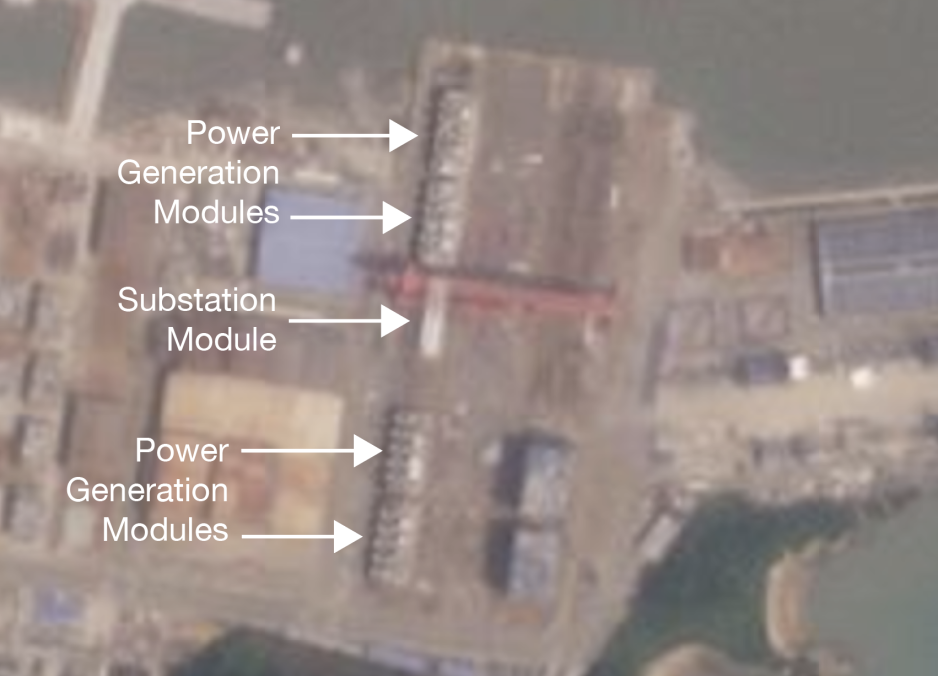

By late summer of 2024 a complex plan had been put into place to transport the modules to the Russian Arctic, the source tells HNN.
The degree to which Wison is directly or indirectly involved in the logistics scheme could not be independently confirmed. What is clear is that Wison manufactured the modules and allowed for them to be loaded at its Zhoushan facility in recent weeks.
In repeated conversations between Wison New Energy and HNN the company advised that it “has discontinued all ongoing Russian projects, including the delivery of any goods to Arctic LNG2.”
However, Wison did not dispute the factual accuracy of HNN’s investigation.
Instead it advised that “Wison has secured binding assurances from its partners that any Wison modules will not be delivered to Arctic LNG 2, and to the extent those third parties have violated their agreements, Wison will notify these third parties of such breaches and pursue corrective remedies.”
The company reiterated that it “will continue to operate consistently with international policies instituted against Arctic LNG 2.”
A copy of the full statement can be found here.
Picking up the First Module
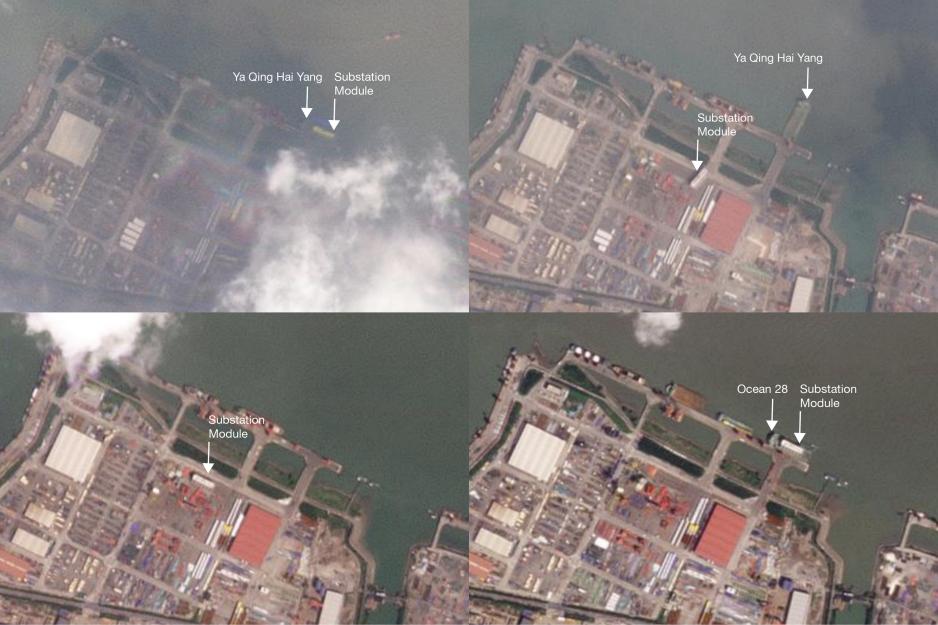
In mid-August a Chinese heavy lift vessel approached Wison’s Zhoushan yard and over the course of about a week the substation module was carefully maneuvered onto the vessel.
The vessel in question is Ya Qing Hai Yang, Chinese-owned and operated. The loading operation was completed around August 23, based on a series of satellite images.

Rather than setting a direct course for the Arctic, Ya Qing Hai Yang carried the substation module around 150 nautical miles to the public port facility at Zhangjiagang Gangxin Heavy Equipment Port Co., where it arrived on or around September 6.
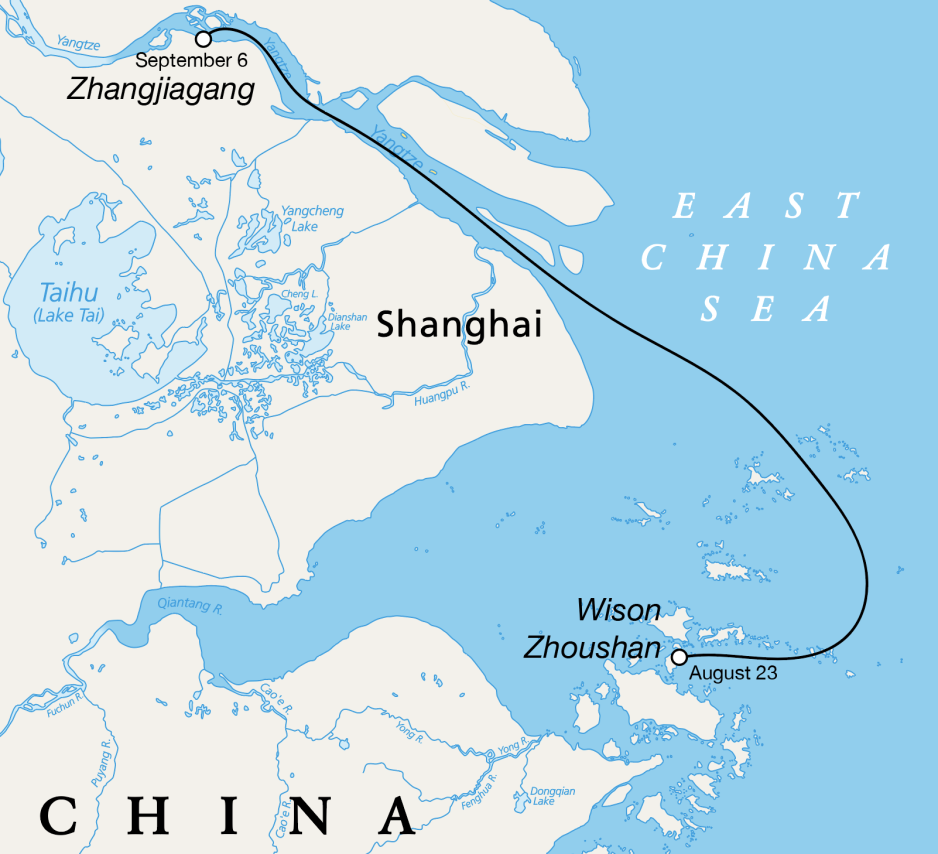
“Wison is afraid of being sanctioned, so they don't want the module to go directly to Russia, so they have found a new port for transshipment,” the source explains.
By offloading and reloading the module at a public port facility, the shipper may hope to create sufficient “distance” between itself and the delivery of any modules to Russia.
A similar line of argument employed by Singaporean shipping operator Red Box carrying modules to Arctic LNG 2, failed to persuade U.S. officials. The company had claimed that it was unaware of the specific cargo it was carrying and it was simply a third party service provider. The company and its two vessels Audax and Pugnax were sanctioned in May 2024.
A series of satellite images shows the offloading of the module, its repositioning at the yard, and subsequent reloading.

An “East China Sea” Paint Job
While the substation module remained at the Zhangjiagang port facility, Ya Qing Hai Yang underwent a “maritime magic trick” as one analyst describes it to HNN.
Ya Qing Hai Yang returned to Zhangjiagang as the newly renamed Ocean 28.
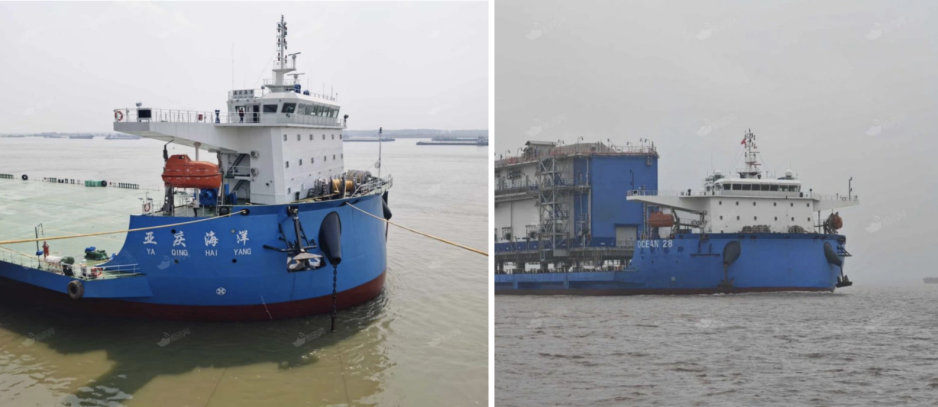

Photos of heavy lift vessel Ya Qing Hai Yang and renamed as Ocean 28. (Source: HNN)
Photos taken about a week apart show in a striking manner the renaming of the vessel, with its original Chinese name and characters painted over and the new name hastily written above, with blue paint patches covering the old name seemingly still wet.

The practice of painting over a vessel’s name to obscure its true identity has become known as a “Bosporus paint job” used by Russian traders in the waters near Istanbul. In the narrow strait vessels entering or leaving the Black Sea can be easily identified from shore.
Ocean 28 departed from Zhangjiagang with the substation module on September 23, 2024. Its Automatic Identification System (AIS) record confirms its departure date and photos show it carrying the module.
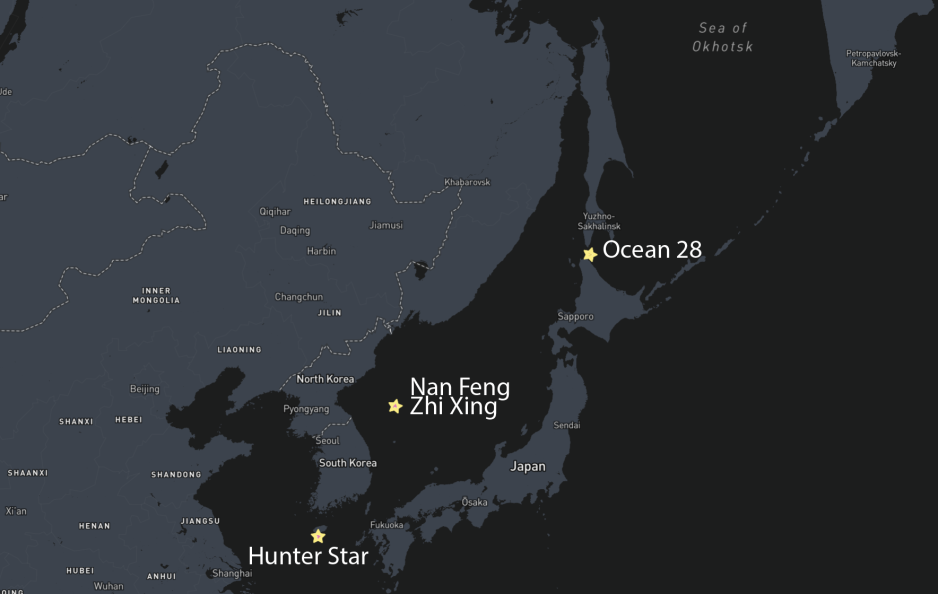
In the days that follow the vessel passes through the East China Sea and travels past the Korean Peninsula. It continues to head north-northeast in the direction of the Bering Strait, where it will take the Northern Sea Route to Arctic LNG 2, sources confirm.
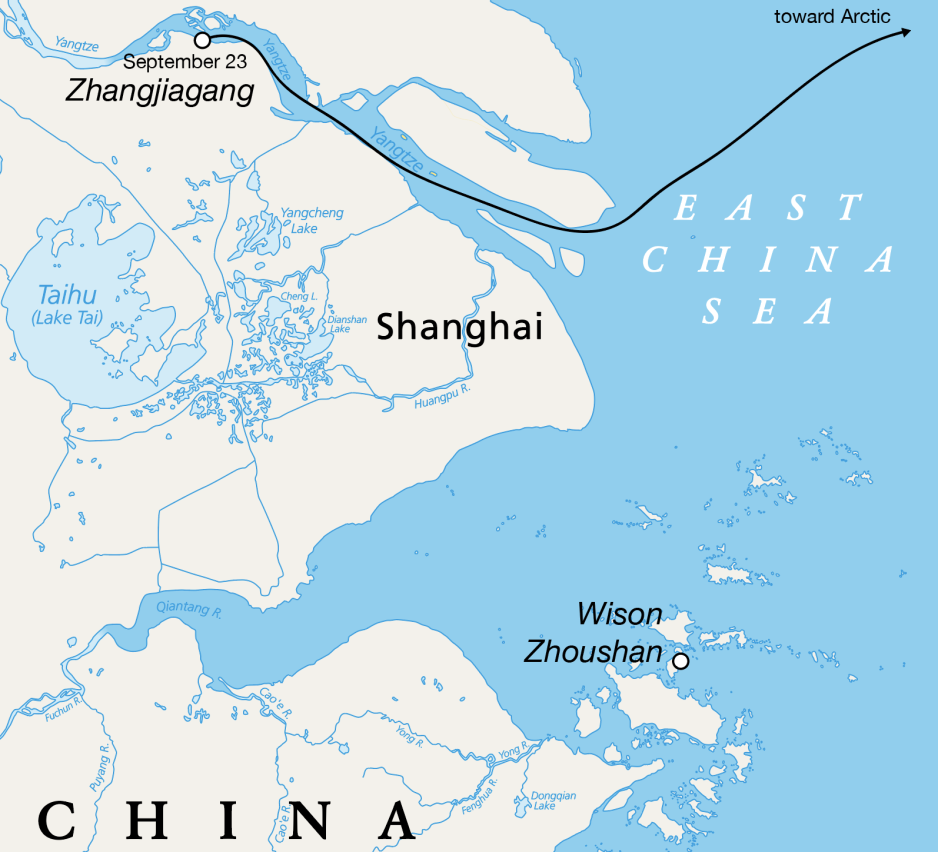
Its AIS currently displays Norway as destination, a common tactic to avoid arousing suspicion previously employed by vessels traveling to Russia.
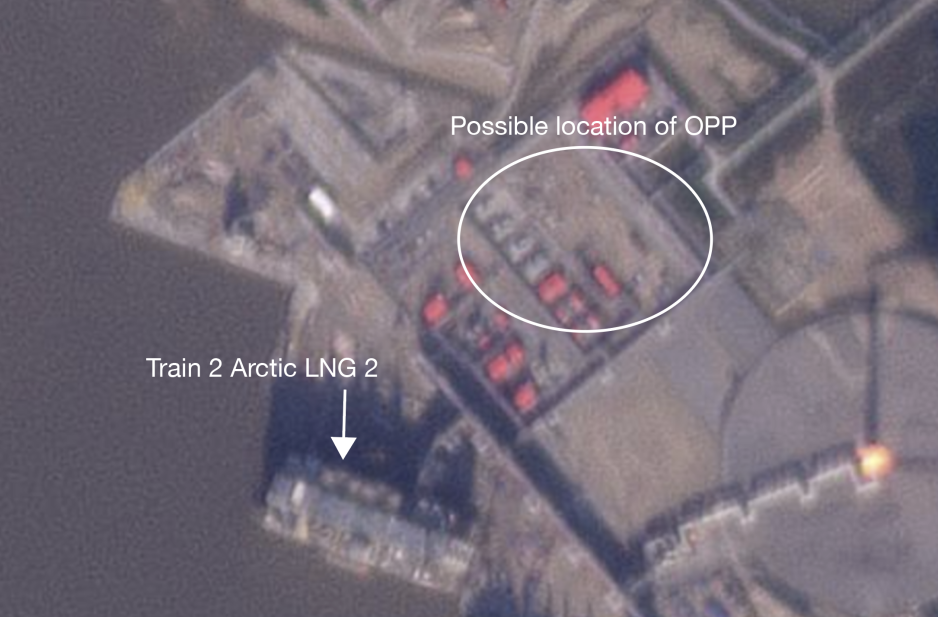
Unlike regular modules for Arctic LNG 2, which were delivered to an assembly yard called Belokamenka near Murmansk, the onshore power plant elements can be installed directly at the Arctic LNG 2 project.
Satellite images suggest that site preparation work may already be underway.
A Wison document seen by HNN showing possible locations for the onshore power plant aligns with the location on the satellite image.

Loading Modules Two and Three

A week after the departure of Ya Qing Hai Yang, the next vessel arrived at Wison’s Zhoushan yard.
The non-propelled barge Si Hang Yong Xing first appeared on satellite images on August 31. The craft is routinely used by Wison to transfer modules between yards.
Over the course of 9 days two power generation modules are loaded onto Si Hang Yong Xing.

The barge subsequently traveled from Zhoushan to Mao Jia Port around 175 nautical miles away.
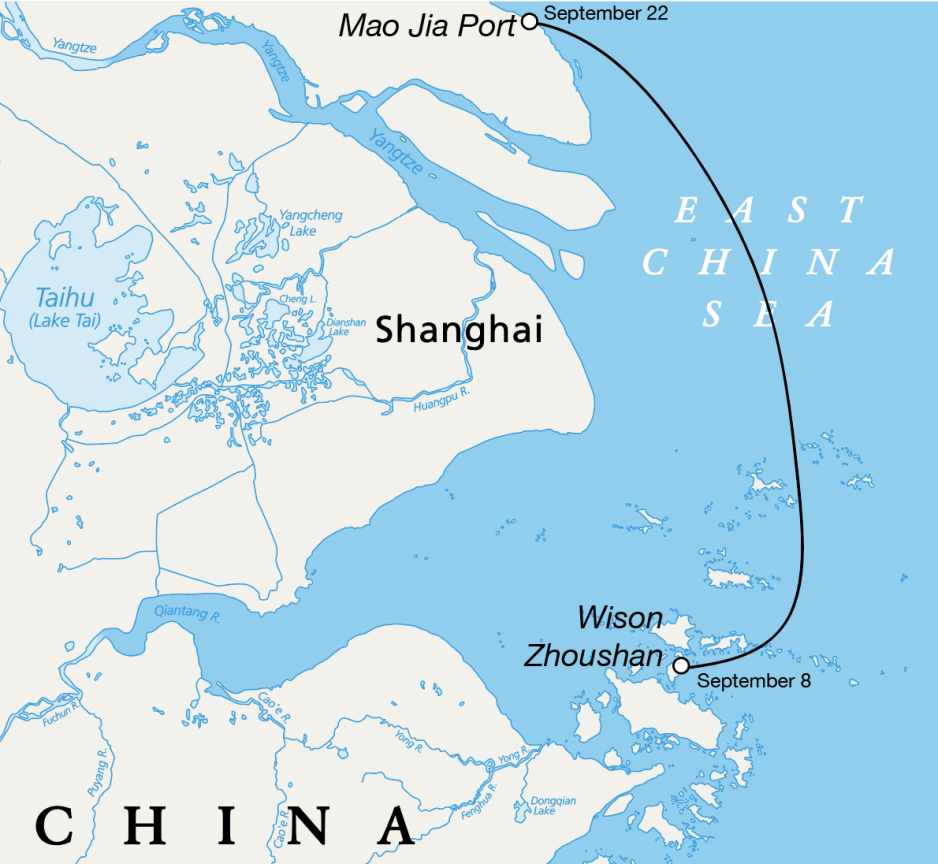
There it was joined by already-sanctioned heavy lift vessel Nan Feng Zhi Xing. Over the course of four days one of the power generation modules is reloaded.
A satellite image taken just before its departure on September 27 shows one power generation module aboard Nan Feng Zhi Xing with the other remaining on Si Hang Yong Xing.
Nan Feng Zhi Xing departed midday on September 27 traveling on the same course as Ocean 28 a week earlier. Its AIS currently displays Vladivostok as a destination, possibly a diversionary tactic.
Nan Feng Zhi Xing was immediately replaced at the dock by Hunter Star, another previously sanctioned heavy lift vessel. AIS tracks confirm its departure and arrival times.
The transfer of the second power generation module onto Hunter Star is completed in around 36 hours and the vessel departed on September 29, following Nan Feng Zhi Xing’s course.
Again, satellite imagery confirms the transfer of the module.

Modules Four and Five Still at Zhoushan

Modules four and five remain at the Zhoushan yard as of September 30, 2024.
With the summer shipping season coming to an end in the Arctic, there may not be sufficient time to ship the final two power generation modules before sea ice blocks the northern shipping lane.
Arctic LNG 2 may be able to start up the second production line at half capacity running on only two power generation units, the source confirms.
How Will the U.S. React?
Over the past 18 months or so the U.S. has been adamant about interdicting the completion of Arctic LNG 2, in an effort to deprive Russia of the revenue associated with the export of LNG.
Given the U.S.’ continued resolve to stop the Arctic LNG 2 it appears likely that this latest attempt to deliver equipment to the project will result in swift action with consequences for Wison, the shipper, or both.
“Attempts to operationalize the sanctioned Arctic LNG 2 project will continue to be met with a swift U.S. government response. Collectively, our actions continue to restrict Russia’s ability to bring the ALNG2 project fully online, said Assistant Secretary Geoffrey R. Pyatt just three weeks ago.
In the process the Departments of State and the Treasury have announced several rounds of sanctions targeting shipping companies, suppliers, and at least one Chinese construction yard – Penglai Jutal Offshore Engineering (PJOE) – supplying modules to Arctic LNG 2.
International sanctions law is complex. At what point does an attempted delivery of sanctioned technology to a blocked project constitute a violation of sanctions?
The three Chinese heavy lift vessels Ocean 28, Nan Feng Zhi Xing, and Hunter Star are weeks away from delivering their problematic cargo to Russian soil.
Could the modules still be recalled in an effort to avoid repercussions?
And who is ultimately legally responsible for their loading? Again, Wison denies any direct involvement and instead points to third parties.
The stakes for Wison New Energies are arguably much higher than for minor shipping companies or suppliers only doing business within China, which limits the impact of sanctions on their operations.
Wison recently signed a $1bn deal with Malaysia's Genting to construct a 1.2m tonnes per annum FLNG facility in West Papua, Indonesia. It also works with Italian energy company ENI on the fabrication of topside modules for a Congo-bound floating LNG unit.
Just last week Wison and Chart Industries, a U.S. provider of liquefaction technology signed a strategic frame agreement to combine their expertise in the LNG industry. Will Wison’s close cooperation with Western companies offer it protection from potential sanctions?
One LNG analyst HNN spoke to aptly concluded: “Wison New Energies is on the rise. How did they think they could play around with sanctions.”



